While it might not be on your radar, the money market is still a crucial part of Nigeria’s financial system — influencing everything from government borrowing to corporate funding. But what exactly is it?
Simply put, the money market is an organized market where governments, financial institutions and other participants trade high-quality financial instruments (like treasury bills and commercial papers) with maturities of one year or less — allowing them to exchange short-term securities for cash.
Whether you’re an investor, a business owner or simply interested in understanding Nigeria’s economy — it’s worth learning about the money market. In this article, we’ll show you how it works, its impact on your financial life and how you can potentially benefit from it by using PiggyVest.
How does the money market work exactly?

The money market functions like a bustling marketplace where financial instruments (different tools that people use to save, invest or borrow money — like stocks and bonds) are the hot commodities. Picture the Nigerian government as a vendor in this market, needing to raise money to pay salaries or fund projects.
They offer instruments like treasury bills (a legal IOU) to investors who are looking for a safe place to loan their money and earn a little interest. These investors can be individuals, businesses or even other banks with spare cash who purchase these instruments with the expectation of getting their money back with interest after a short period (typically 91, 182, or 364 days).
But what’s the trading process like in the money market?
Well, banks and discount houses act as intermediaries — connecting buyers and sellers while facilitating smooth transactions.
When the government or a company wants to raise money, they announce the issuance of these instruments at a specific price. Interested investors then submit bids, indicating how much they want to buy and the interest rate they’re willing to accept.
The issuer (the government or a company) then allocates the instruments to the highest bidders who offered the lowest interest rates. After they’re issued, these instruments can be traded in the secondary market, where prices fluctuate based on supply and demand — similar to how the price of goods might change in a regular market.
When the instrument reaches maturity, the issuer pays back the original amount plus the agreed-upon interest to whoever holds the instrument.
Let’s use a simple example to illustrate what we mean.
Let’s say the Nigerian government needs ₦100 million to pay salaries. They issue treasury bills (aka T-bills) with a face value of ₦100 each and a maturity of 91 days. You, as an investor, purchase ₦10,000 worth of T-bills.
After 91 days, the government will pay you back your ₦10,000 plus a little interest.
What are the features of the money market?

As we mentioned, the money market provides a platform for short-term borrowing and lending — allowing participants to manage their short-term cash needs efficiently. However, before we go any further, it’ll be beneficial to explore exactly what sets the money market apart from other financial markets.
Here are some of the distinct features of the money market:
How To Invest In Real Estate In Nigeria (Even If You’re Not Rich Yet): 5 Ways For Beginners To Get Involved

- High liquidity: The money market provides investors with a high level of liquidity, allowing them to easily convert their investments into cash.
- Short-term maturity: The instruments traded in the money market have relatively short maturity periods, usually ranging from overnight to one year.
- Low risk: Investments in the money market are generally considered low-risk due to the short maturity periods and the financial stability of the issuers, such as the government and reputable financial institutions.
- Low return: As a trade-off for the low risk, money market investments typically offer lower returns compared to riskier assets like stocks or long-term bonds.
Additionally, most transactions in the money market are conducted on a wholesale basis between financial institutions and corporations. That said, who exactly participates in the money market?
Who are the participants in the money market?

By participating in the money market, entities can access funds quickly and at competitive rates — enabling them to meet their liquidity requirements without having to resort to long-term borrowing. But who exactly are these entities?
The money market comprises the following participants:
- Commercial banks. They play a significant role in facilitating short-term borrowing and lending activities.
- Discount houses. These specialized institutions act as intermediaries between banks and other participants in the market.
- Non-bank financial institutions. Examples include insurance companies, pension funds and asset management firms that invest surplus funds in the money market.
- The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN). As the regulator of the financial system, the CBN actively participates in the money market to influence liquidity and implement monetary policies. A great example is the recent increase in monetary policy rate from 26.25% in June 2024 to 26.75 in July 2024
- Individual investors. They can invest in money market funds, which pool money from multiple investors to purchase a variety of money market instruments.
- Governments. They issue short-term debt instruments like treasury bills to finance their short-term funding needs.
- Corporations. They issue commercial paper to raise short-term capital for working capital and other operational expenses.
Now, let’s dive even further. Why is the money market important? Why does it exist?
What is the importance of the money market?

The money market performs several vital functions that contribute to the stability and efficiency of the overall financial system.
Here are some of the reasons why the money market is vital:
What Is Diversification In Investing? Tips For Building A Lasting Portfolio In Nigeria
- It facilitates liquidity management for financial institutions.
- It provides a platform for short-term borrowing and lending — meeting the funding needs of market participants.
- It acts as a benchmark for determining interest rates in the economy.
- It assists the government in managing its short-term financing requirements and controlling liquidity levels.
- It plays a crucial role in influencing monetary policy decisions since the CBN often uses it as a tool to implement and regulate monetary policies.
- It provides a significant source of investment opportunities for individuals and institutions looking to park their excess funds in low-risk, short-term financial instruments.
This list isn’t exhaustive, of course. However, it does highlight the major ways the money market impacts a country’s financial system.
What are money market instruments?
We’ve mentioned treasury bills and commercial papers, but these aren’t the only instruments traded in the money market. In Nigeria, for example, there are several instruments (or securities) that participants can trade with at any given time.
Some of the instruments in the money market are:
- Banker’s Acceptance (BAs). These are time drafts drawn on and accepted by banks, indicating the bank’s commitment to repay the amount on maturity.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs). These are time deposits offered by banks with fixed maturity dates and interest rates.
- Commercial Papers (CPs). These are unsecured promissory notes issued by reputable companies to raise short-term funds.
- Repurchase Agreements (Repos). These are short-term loans where one party sells securities to another with an agreement to repurchase them at a slightly higher price.
- Treasury Bills (T-Bills). These are short-term government securities issued by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) to finance the government’s immediate cash flow needs.
The ones on this list are the most common, but the Nigerian money market also features other notable financial products that cater to various investment needs.
Are money markets savings or investments?

Money markets primarily serve as investment avenues for individuals and institutions with surplus funds. These investors preserve capital and earn modest returns by trading financial instruments which generate interest.
However, they can also earn profits in the form of discount income or coupon payments.
One small reminder: money market securities are considered conservative investments since they appeal to risk-averse investors seeking liquidity and short-term stability. However, these instruments also offer interest rates that are typically lower than those associated with longer-term investments or higher-risk assets (like shares).
How Do The Real Estate Investment Opportunities On Piggyvest Work?


How to invest in the money market with PiggyVest’s Investify
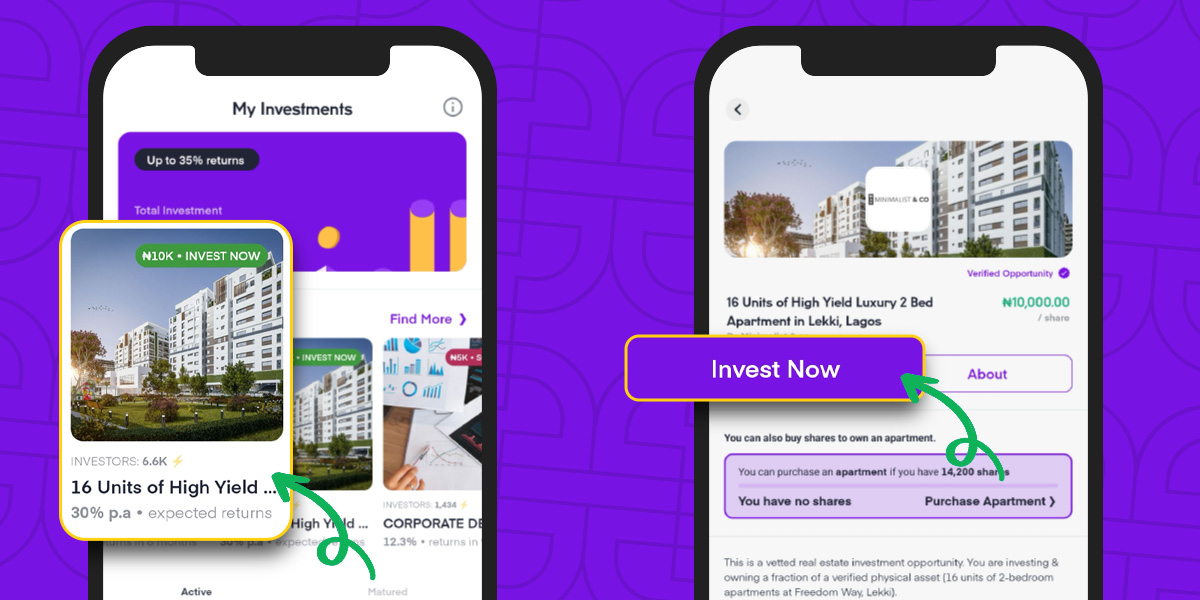
Did you know that you can invest in the money market right now on PiggyVest? Investify allows you to earn up to 35% annual interest by parking your funds in safe, low-to-medium risk, primary and secondary investment opportunities.
Here’s how you can invest in the money market using Investify:
- Log in to your PiggyVest app.
- Go to “Invest” and choose an investment opportunity.
- Click on “Invest Now.”
- Type in the number of units you want to buy and click on “Next Step.”
- Confirm your Investment.
- Click on “Invest Now.”
It’s that easy!
Is forex a money market?

Forex (or foreign exchange) is not part of the money market. The money market primarily deals with short-term borrowing and lending of funds through specified instruments, as we mentioned earlier.
However, forex involves the trading of currencies — enabling individuals, businesses and institutions to exchange one currency for another.
Forex trading is one of the largest financial markets globally — with a daily trading volume exceeding trillions of dollars. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week and across different time zones — allowing for continuous trading and liquidity.
Additionally, the forex market is decentralised — meaning there is no central exchange or regulator — and you conduct trades over-the-counter.
Is the money market the same as the stock market?
The money market is not the same as the stock market. While the money market focuses on short-term borrowing and lending of funds (primarily involving low-risk instruments, as we discussed earlier), the stock market deals with issuing and trading long-term equities (like stocks).
Despite their differences, both markets contribute to the overall functioning and stability of the financial system.
Summary
The money market in Nigeria plays a critical role in the financial system, offering participants a platform for short-term borrowing, lending and investment activities. Additionally, it provides liquidity, facilitates efficient cash flow management, and acts as a benchmark for interest rates.
As an investor, you can benefit from the money market by understanding how its various instruments work and making informed financial decisions.
The articles on the PiggyVest Blog are developed by seasoned writers who use original sources like authoritative websites, news articles and academic journals to perform in-depth research. An experienced editor fact-checks every piece before it is published to ensure you are always reading accurate, up-to-date and balanced content.
- Channels: CBN Raises Interest Rate To 26.75% Amid Soaring Inflation
- CBN: Money Market Indicators (In Percentage)
- CBN: Government Securities Summary
- CBN: Frequently Asked Questions